Biology Notes for Class 12
Chapter 4: Reproductive Health
Chapter Summary
Reproductive health refers to a total well-being in all aspects of reproduction, i.e., physical, emotional, behavioural and social. Our nation was the first nation in the world to initiate various action plans at national level towards attaining a reproductively healthy society.
Counselling and creating awareness among people about reproductive organs, adolescence and associated changes, safe and hygienic sexual practices, sexually transmitted infections (STIs) including AIDS, etc., is the primary step towards reproductive health. Providing medical facilities and care to the problems like menstrual irregularities, pregnancy related aspects, delivery, medical termination of pregnancy, STIs, birth control, infertility, post natal child and maternal management is another important aspect of the Reproductive and Child Health Care programmes.
An overall improvement in reproductive health has taken place in our country as indicated by reduced maternal and infant mortality rates, early detection and cure of STIs, assistance to infertile couples, etc. Improved health facilities and better living conditions promoted an explosive growth of population. Such a growth necessitated intense propagation of contraceptive methods. Various contraceptive options are available now such as natural, traditional, barrier, IUDs, pills, injectables, implants and surgical methods. Though contraceptives are not regular requirements for reproductive health, one is forced to use them to avoid pregnancy or to delay or space pregnancy.
Medical termination of pregnancy is legalised in our country. MTP is generally performed to get rid of unwanted pregnancy due to rapes, casual relationship, etc., as also in cases when the continuation of pregnancy could be harmful or even fatal to either the mother, or the foetus or both.
Infections or diseases transmitted through sexual intercourse are called Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STIs). Pelvic Inflammatory Diseases (PIDs), still birth, infertility are some of the complications of them. Early detection facilitate better cure of these diseases. Avoiding sexual intercourse with unknown/multiple partners, use of condoms during coitus are some of the simple precautions to avoid contracting STIs.
Inability to conceive or produce children even after 2 years of unprotected sexual cohabitation is called infertility. Various methods are now available to help such couples. In Vitro fertilisation followed by transfer of embryo into the female genital tract is one such method and is commonly known as the ‘Test Tube Baby’ Programme.
REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH – PROBLEM AND STRATERIES:
Ø The programme “family planning” initiated in 1951.
Ø Reproductive and child health care (ACH)
Ø Sexually transmitted diseases (STD).
Ø Amniocentesis: A fetal sex determination test based on the chromosomal pattern in the amniotic fluid surrounding the developing embryo.
Ø ‘Saheli’ an oral contraceptive for female, developed by CDRI.
POPULATION EXPLOSION AND BIRTH CONTROL:
Ø Increased health facilities, better living conditions are the cause of population explosion.
Ø Out of 6 billion world population 1 billion are Indians.
Ø Rapid decline in death rate, maternal mortalility rate (MMR) and infant mortality rate (IMR) are major cause of population growth.
Ø Indian population growth rate is around 1.7 percent.
Characteristics of ideal contraceptive.
Ø User friendly.
Ø Easily available.
Ø Effective
Ø Nor or least side – effects.
Ø No way interferes with sexual drive.
BIRTH CONTROL METHODS:
i. Natural methods:
Ø work on the principle of avoiding chances of ovum and sperms meeting.
ii. Periodic abstinence:
Ø Avoid or abstain from coitus form day 10 to 17 of the menstrual cycle when ovulation could be expected.
Ø Chance of fertilization is very high in this period.
Ø It is called fertile period.
iii. Withdrawal or coitus interruption:
Ø The male partner withdraws his penis from the vagina just before ejaculation, so as to avoid insemination into the vagina.
iv. Lactational amenorrhea:
Ø No menstruation during lactation period.
Ø Chance of fertilization is nil.
Ø It is effective upto six month.
v. Barrier methods:
Ø Principle of working: prevents physical meeting of sperm and ovum.
Ø Such methods available both for male and female.
vi. Condoms:
Ø Barriers made of thin rubber/latex sheath.
Ø Used to cover the penis in male or vagina and cervix in the female.
Ø Used just before coitus so that semen not entered into the female reproductive tract.
Ø Male and female condoms are disposable.
Ø Prevents AIDS and STDs.
vii. Diaphragm, cervical caps and vaults:
Ø Barriers made of rubber.
Ø Inserted into the female reproductive tract to cover the cervix.
Ø Prevents conception by blocking the entry of sperm through cervix.
Ø They are reusable.
viii. Intra Uterine Devices:
Ø These devices are only used by female.
Ø Inserted by doctor or by expert nurses in the uterus through vagina.
Ø Non-medicated IUDs e.g. Lippes loop.
Ø Copper releasing IUDs (CuT, Cu7, Multiload 375)
Ø Hormone releasing IUDs (Progestasert, LNG-20)
Principle of working:
Ø Increase phagocytosis of sperm within the uterus.
Ø Cu ion released suppresses sperm motility and fertilizing capacity of sperm.
Ø Hormone releasing IUDs make the uterus unsuitable for implantation and the cervix hostile to the sperm.
ix. Oral contraceptives:
Ø This methods used by female only.
Ø Used in the form of tablets hence popularly called pills.
Ø Pills contain progestogens or progestogen-estrogen combination.
Ø Pills have to be taken daily for a period of 21 days.
Ø Started within first five days of menstruation.
Ø Pills are very effective with lesser side effect.
Ø Saheli- a non steroidal preparation used as oral contraceptive pills.
Principle of working:
Ø Inhibit ovulation.
Ø Inhibit implantation.
Ø Alter the quality of cervical mucus to prevent/retard entry of sperms.
x. Injections or implants:
Ø Progestogens alone or in combination with estrogen used as injections or implants under the skin by female.
Ø Mode of action is similar as in pills
Ø It is very effective for long periods.
xi. Emergency contraceptives:
Ø These methods are used within 72 hours of coitus, rape or casual unprotected intercourse.
Ø Administration of progestogens or progestogen-estrogen combination.
Ø Use of IUDs.
xii. Surgical Methods:
Ø It is also called as sterilization method.
Ø Advised to both male and female partner.
Ø Permanent or terminal method to prevent pregnancy.
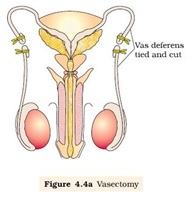
Ø Sterilization process in male is called ‘vasectomy,
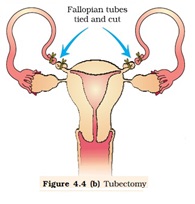
Ø Sterilization process in female is called ‘Tubectomy’
Ø In vasectomy, a small part of the vas deferens is removed or tied up.
Ø In Tubectomy a small part of the fallopian tube is removed.
Ø Reversibility is very poor.
MEDICAL TERMINATION OF PREGNANCY:
Ø Intentional or voluntary termination of pregnancy before full term is called medical termination of pregnancy (MTP) or induced abortion.
Ø MTP has significant role in decreasing population.
Ø It accounts for 1/5th of the total number of conceived pregnancies.
Ø Legal restriction only to reduce female foeticide.
Ø This method is safe within 1st trimester.
SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES:
Ø Diseases or infections which are transmitted through sexual intercourse.
Ø Also known as Venereal diseases (VD) or reproductive tract infections (RTIs)
Ø Gonorrhea, Syphilis, Genital herpes, chlamydiasis, genital warts, trichomoniasis, hepatitis- B and HIV are some common STDs.
Ø Except hepatitis-B, genital herpes and HIV infections, others are curable.
Symptoms:
Ø Itching, fluid discharge, slight pain, swelling in the genital region.
Ø STDs remain asymptomatic in female and remain undetected for long.
Ø In the later stage it may leads to Pelvic inflammatory diseases (PID), abortion, still births, ectopic pregnancy, infertility or even cancer in RT.
Preventions:
Ø Avoid sex with unknown partners/ multiple partners.
Ø Always use condoms during coitus.
Ø In case of doubt, consult with a qualified doctor for early detection.
Ø Get complete treatment if diagnosed with disease.
INFERTILITY:
Ø The couple unable to produce children inspite of unprotected sex.
Ø The reason of infertility may be:-
- physical,
- congenital,
- diseases,
- drugs,
- immunological or
- Even psychological.
Ø Problems of infertility may be in male or female.
Ø Infertility clinic can diagnose and correct the cause of infertility.
Ø In case there no corrections are possible, some special technologies used to have children called assisted reproductive technologies. (ART)
Assisted reproductive technologies:
(a) In vitro fertilization:
Ø Fertilization outside the body in the laboratory.
Ø Condition created in laboratory similar to the body.
(b) Embryo transfer:
Ø Popularly known as test tube baby programme.
Ø Ova from the wife/donor and sperm from the husband/donor are collected and induced to form zygote under simulated conditions in the laboratory.
Ø The zygote or early embryos (with upto 8 blastomeres) could be transferred into the fallopian tube.
Ø ZIFT- Zygote intra fallopian transfer.
Ø IUT- Intra Uterine transfer (embryo with more than 8 blastomeres).
Ø Further development taken place within the female body.
Ø Embryo formed by in-vivo fertilization can also be transfer to assist those female who cannot conceive.
(c) Gamete intra fallopian transfer- GIFT
Ø Transfer of ovum collected from the donor into the fallopian tube of another female who cannot produce it.
Ø Such female can provide suitable environment for fertilization and development.
(d) Intra cytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI):
Ø The sperm is directly injected into the ovum.
Ø After in vitro fertilization either ZIFT or embryo transfer technique is followed.
(e) Artificial insemination (AI)
Ø Semen is collected either from the husband or donor is artificially introduced into vagina or into the uterus (IUI-intra uterine insemination) of the female.
Ø Such technology is useful in cases either the male partner unable to inseminate the female or very low sperm counts in the ejaculates.
Abbreviation:
Ø IUCD: Intra Uterine Contraceptive Device
Ø RCH: Reproductive and Child Health care
Ø STD: Sexually Transmitted Disease
Ø HIV: human Immuno deficiency virus.
Ø AIDS: Acquired immuno deficiency syndrome
Ø CDRI: Central Drug Research Institute
Ø MMR: Maternal Mortality Rate
Ø IMR: Infant mortality rate.
Ø MTP: Medical Termination of Pregnancy
Ø VD: Venereal Disease
Ø RTI: Reproductive Tract Infection
Ø PID: Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Ø ART: Assisted Reproductive Technologies
Ø IVF: In Vitro Fertilisation
Ø ZIFT: Zygote Intra Fallopian Transfer
Ø AI: Artificial insemination
Ø IUI: Interna uterine insemination.
Ø ET: Embryo transfer.
Ø IUT: intra uterine transfer.
Ø ICSI: Intra Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection.
Disclaimer: All contents are originally prepared by Shri K C Meena Ji, Principal, KVS.
Amazon Affiliate Disclaimer: cbsecontent.com is a part of Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.in. As an amazon associates we earn from qualifying purchases.











Good post! We will be linking to this particularly great post on our site. Keep up the great writing
I very delighted to find this internet site on bing, just what I was searching for as well saved to fav